 Image 1 of
Image 1 of


Cortisol Testing
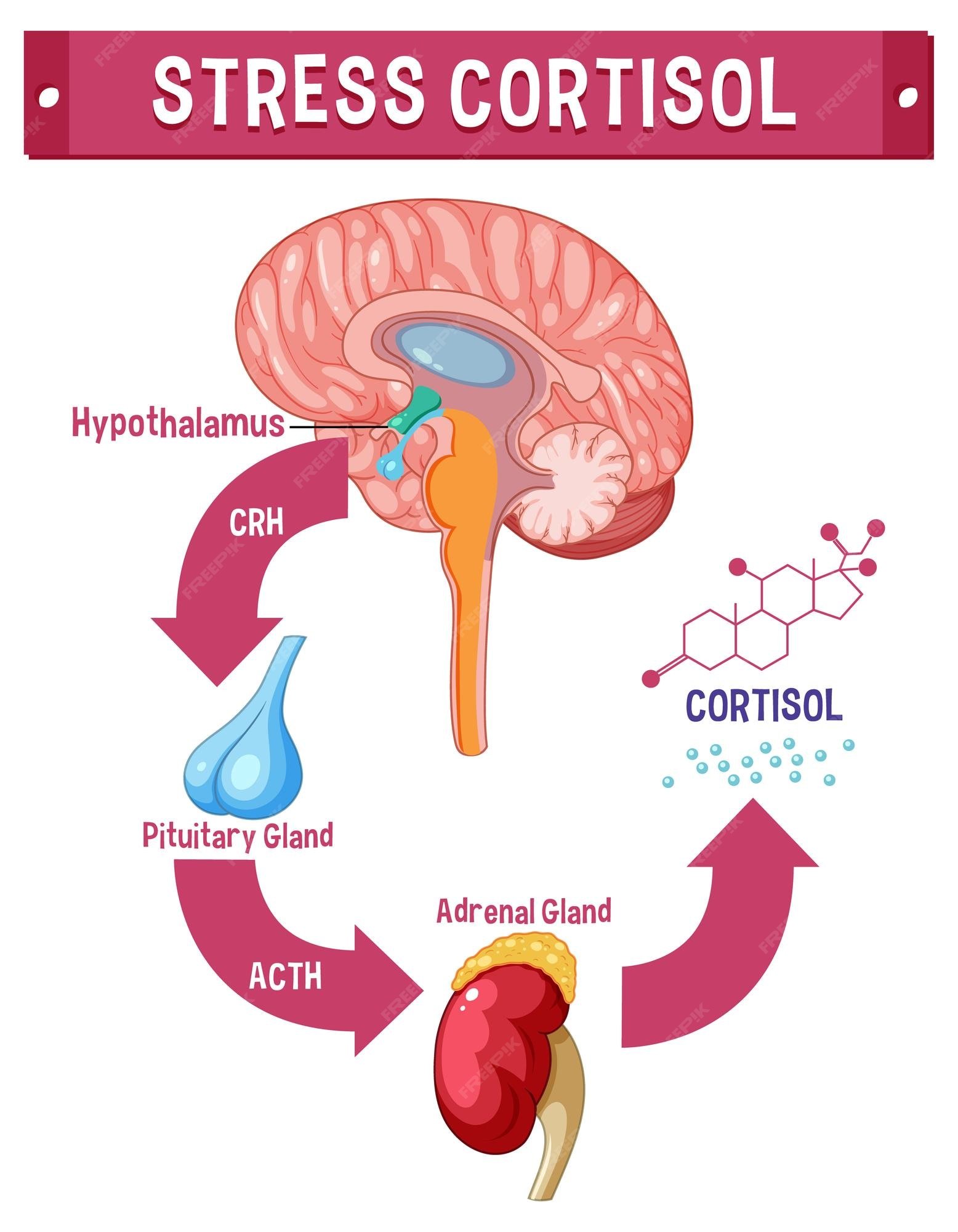
Cortisol is released by the adrenal gland following the stimulation by ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) which is produced by the anterior pituitary gland. This gland is itself triggered by corticotropin-releasing hormone produced by the hypothalamus. The process is called the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis.
Measurement of cortisol can be done in saliva, blood and urine. These matrices reflect current levels in the body. Long term levels as measured in hair may allow assessments relating to causation of chronic diseases based on a continuous activation of the HPA axis.
Hair analysis for cortisol is seen as a new tool for the diagnosis of these diseases. Hair cortisol measurements have been validated by repeated measurements of saliva and urine. Hair cortisol has also been linked to chronic stress and mental health disorders.
The hair matrix allows the measurement of free cortisol for periods up to six months. Beyond this time the cortisol levels are lower due to the amount of washing the hair has been submitted to.
General observations relating to cortisol levels in hair the Whitehall II Study:
In general women have lower levels than men
Higher levels seen with diabetes
Higher in blacks than other ethnic groups - possibly because of hair being coarser seems to increase cortisol levels (in-house study)
Depressive symptoms were associated with elevated levels although prolonged depression like PTSD showed lower levels
Age did not show differences in levels when corrected for diseases
Taking corticosteroids generated lower hair levels of cortisol
High BMI individuals had higher cortisol levels5
Dyed hair had lower cortisol levels
Lower cortisol levels seen in seasons other than winter
Cortisol is released by the adrenal gland following the stimulation by ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) which is produced by the anterior pituitary gland. This gland is itself triggered by corticotropin-releasing hormone produced by the hypothalamus. The process is called the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis.
Measurement of cortisol can be done in saliva, blood and urine. These matrices reflect current levels in the body. Long term levels as measured in hair may allow assessments relating to causation of chronic diseases based on a continuous activation of the HPA axis.
Hair analysis for cortisol is seen as a new tool for the diagnosis of these diseases. Hair cortisol measurements have been validated by repeated measurements of saliva and urine. Hair cortisol has also been linked to chronic stress and mental health disorders.
The hair matrix allows the measurement of free cortisol for periods up to six months. Beyond this time the cortisol levels are lower due to the amount of washing the hair has been submitted to.
General observations relating to cortisol levels in hair the Whitehall II Study:
In general women have lower levels than men
Higher levels seen with diabetes
Higher in blacks than other ethnic groups - possibly because of hair being coarser seems to increase cortisol levels (in-house study)
Depressive symptoms were associated with elevated levels although prolonged depression like PTSD showed lower levels
Age did not show differences in levels when corrected for diseases
Taking corticosteroids generated lower hair levels of cortisol
High BMI individuals had higher cortisol levels5
Dyed hair had lower cortisol levels
Lower cortisol levels seen in seasons other than winter
Cortisol is released by the adrenal gland following the stimulation by ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) which is produced by the anterior pituitary gland. This gland is itself triggered by corticotropin-releasing hormone produced by the hypothalamus. The process is called the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis.
Measurement of cortisol can be done in saliva, blood and urine. These matrices reflect current levels in the body. Long term levels as measured in hair may allow assessments relating to causation of chronic diseases based on a continuous activation of the HPA axis.
Hair analysis for cortisol is seen as a new tool for the diagnosis of these diseases. Hair cortisol measurements have been validated by repeated measurements of saliva and urine. Hair cortisol has also been linked to chronic stress and mental health disorders.
The hair matrix allows the measurement of free cortisol for periods up to six months. Beyond this time the cortisol levels are lower due to the amount of washing the hair has been submitted to.
General observations relating to cortisol levels in hair the Whitehall II Study:
In general women have lower levels than men
Higher levels seen with diabetes
Higher in blacks than other ethnic groups - possibly because of hair being coarser seems to increase cortisol levels (in-house study)
Depressive symptoms were associated with elevated levels although prolonged depression like PTSD showed lower levels
Age did not show differences in levels when corrected for diseases
Taking corticosteroids generated lower hair levels of cortisol
High BMI individuals had higher cortisol levels5
Dyed hair had lower cortisol levels
Lower cortisol levels seen in seasons other than winter
